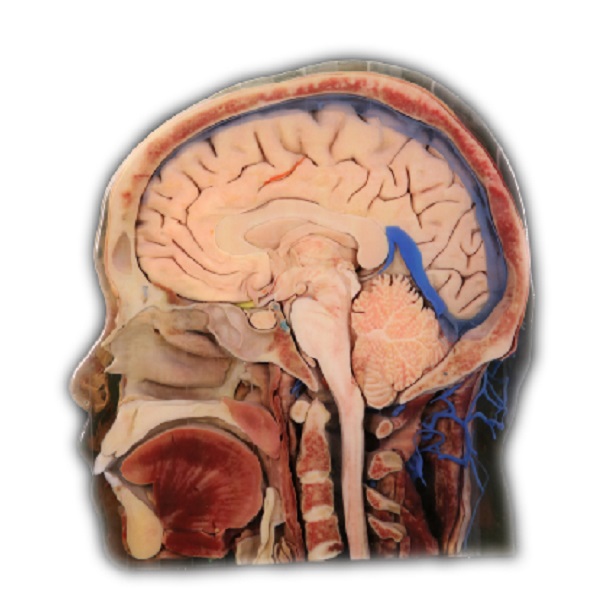
In recent years, the emergence of virtual reality (VR) technology has revolutionized various industries. One remarkable application is the vr anatomy table, which offers a unique and immersive learning experience for medical professionals and students alike.
The Advantages of VR Anatomy Table

The VR anatomy table provides an innovative approach to studying human anatomy. With its advanced 3D visualization capabilities, users can explore detailed anatomical structures in a realistic virtual environment. This interactive tool allows for hands-on exploration and manipulation of anatomical models, enhancing understanding and retention of complex concepts.
Furthermore, the VR anatomy table offers a collaborative learning experience. Multiple users can simultaneously interact with the virtual models, facilitating group discussions and knowledge sharing among peers. This fosters teamwork skills while encouraging active engagement in the learning process.
DIGIHUMAN: A Breakthrough in Virtual Anatomy
A notable example of a cutting-edge VR anatomy table is DIGIHUMAN. Developed by leading experts in medical imaging technology, DIGIHUMAN provides highly accurate representations of human bodies based on real patient data.
With DIGIHUMAN’s advanced algorithms and high-resolution imaging techniques, it creates lifelike digital replicas that accurately depict anatomical structures down to minute details. Users can navigate through different layers such as muscles, organs, and skeletal systems with ease using intuitive controls.
Augmented Reality Anatomy: Expanding Possibilities
In addition to VR anatomy tables’ benefits mentioned earlier, augmented reality (AR) technology adds another dimension to this educational tool. By overlaying digital information onto real-world environments through AR headsets or mobile devices, learners can visualize internal body structures directly on physical objects or even their own bodies.
This integration between virtual content and the real world enhances spatial understanding and enables learners to grasp anatomical relationships more effectively. It also allows for interactive quizzes, simulations, and guided tutorials, making the learning experience even more engaging and personalized.
Conclusion
The VR anatomy table presents a groundbreaking solution for medical education. Its immersive nature, collaborative features, and integration with technologies like DIGIHUMAN and augmented reality anatomy offer unparalleled advantages in teaching human anatomy. By embracing these advancements, medical professionals and students can enhance their knowledge retention, improve critical thinking skills, and ultimately contribute to better patient care in the future.